Experimental Mine Barbara (ROCCS
in-situ
test site)
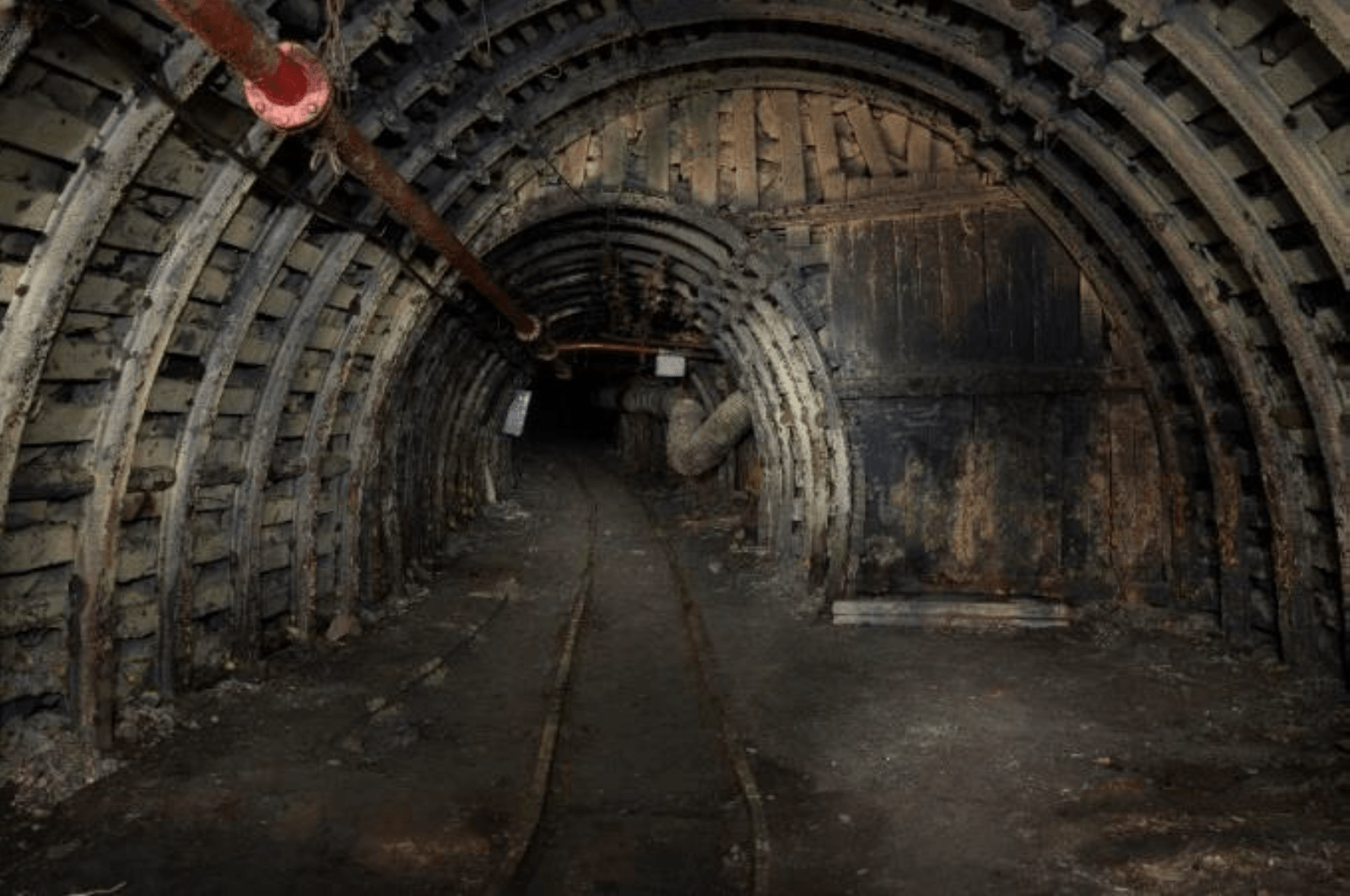
The experimental min "Barbara" is located in the southern Poland in the administrative area of Mikolów City.The Experimental Mine "Barbara" was founded in 1925 by Związek Górniczo-Hutniczy [Mining-Metallurgical Federation]. The Experimental Station and the Central Office of Mining Rescue were transferred to it from Pniowiec. The new post was called the Experimental Mine "Barbara", the Central Office of Mining Rescue and the Magnetic Observatory in Mikołów. After 1933 it was financed from the funds of the Experimental Mine "Barbara" Association. Since the end of World War 2, the mine has worked as one of the main components of the projects of the Central Mining Institute (GIG).
The "Barbara" mine is the only research and scientific post in Poland and in Europe, with an experimental range for testing devices, equipments, materials and procedures in real underground conditions.
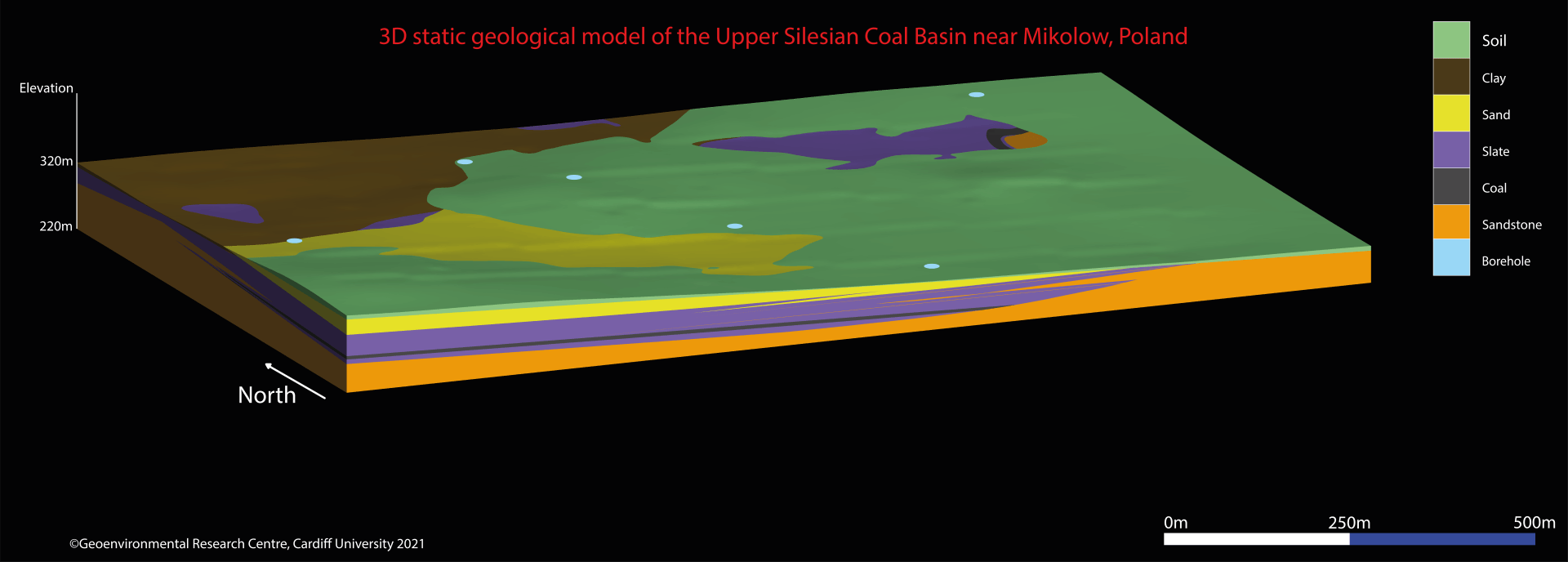
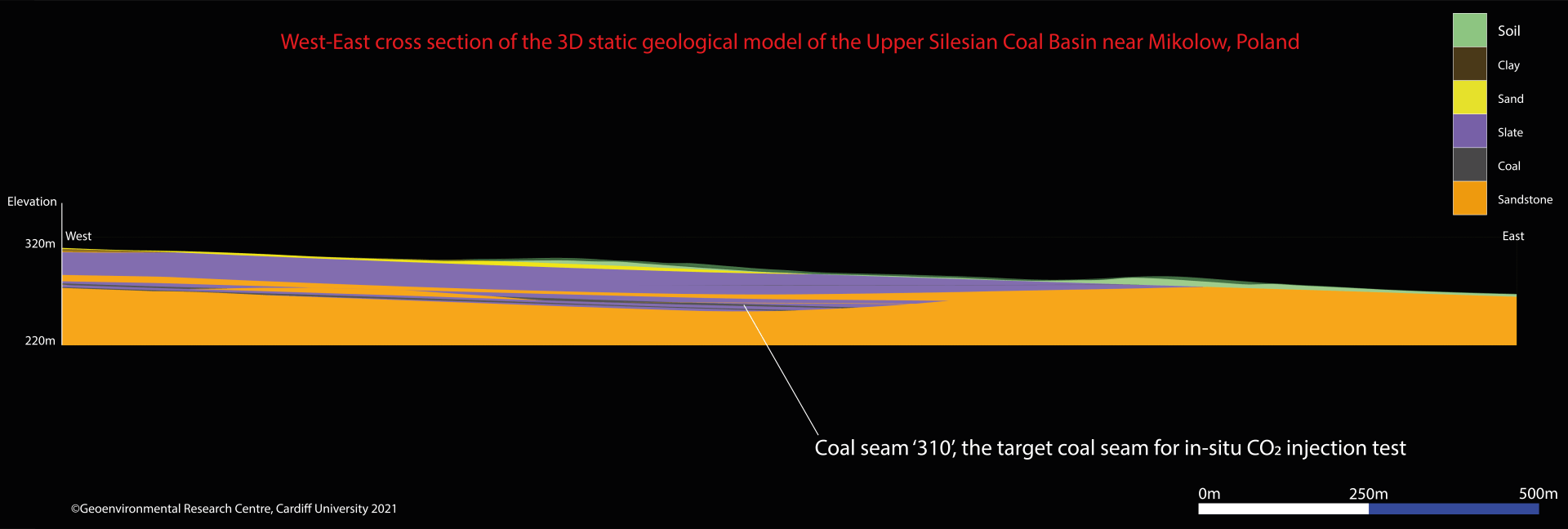
The geological structure of the rock mass dates back to Quaternary period and productive Carboniferous. Carboniferous layers are overlapped by Quaternary formations, represented by Orzesze Beds, and fragmentarily by Laziska Beds.Quaternary sediments are composed of sand, gravel and clay. The Quaternary cover is thickest in the northern part of the mine area whereas a clay formation is mostly present in the southeastern region of this area. Carboniferous layers, represented by Laziska Beds, exist only in a small area in the southwestern part of the mine area and consists of sandstones and conglomerates. The Laziska Beds are approximately 30 m in thickness. In the rest of the mining area, directly under the Quaternary formations, Orzesze Beds occur, and these beds are represented by silty shale, fine and medium grained sandstone and hard coal seams.
Lithological formation of rocks is heterogeneous. Layers are formed from alternating fine and medium grained sandstones and shale among which numerous coal seams can be found. The most stable as for their expansion and volume are the seams 308, 310 and 318.
The rock surrounding coal seams create a rock mass of very heterogeneous geological properties caused by the micro and macro fissures and interchangeable appearance of mudstone and sandstone. There is no vibration impact from plate tectonics.
Hydrological investigations showed that two groundwater aquifers exist in the mining area of the EM “Barbara.” The first aquifer was built from sand, and in this aquifer, the water table is stabilised from 0.3 m below the land surface in the northwestern region to 10 m below the land surface in the southeastern part of the mining area. The second aquifer exists in Upper Carboniferous sediments, and its scope encompasses the target coal seam. This aquifer is sub-artesian with a groundwater level of 12 m below the land surface, and it exists mainly in fine and medium grained sandstone layers.
Geological Model of Barbara Mine
ROCCS is funded by the European Union Research Fund for Coal and Steel (EU- RFCS) under the grant agreement No 899336
© 2020 ROCCS. All Rights Reserved.